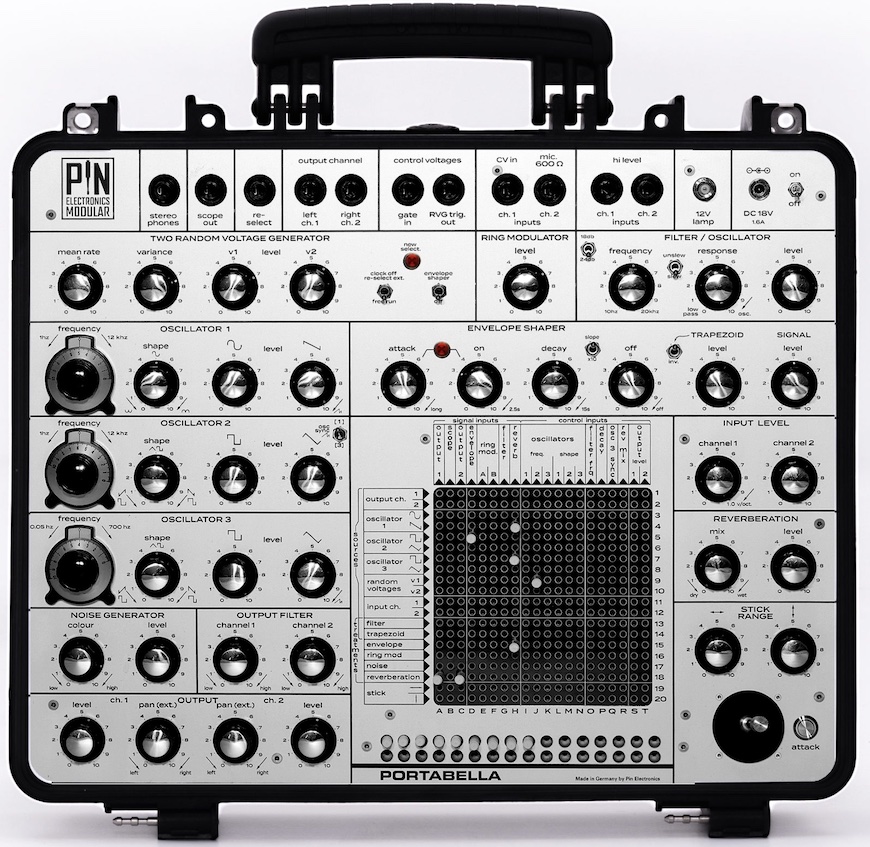
We lost another. Some sad news in via Atomic Shadow:
"I learned this morning of the passing of my best friend, Stephen Howell. Many of you know of his work as Hollow Sun. He was a well respected sound designer who had worked for Peter Gabriel and many others. He was a long time fixture at Akai Professional where he designed the UI for many of their top products as well as producing the sample content.
Stephen was my mentor and gave me the nudge to take my music in to a totally abstract direction. Without him there would have been no Atomic Shadow project. I plan to write a bit more about him when I can think more clearly. I am closing down yesterday's world of tomorrow, at least for now.
We only produced one piece of music together. I always tried to get him to do more of his own music, but he said that making music did not pay the bills. He was correct of course. I cut together a video to go with it at the time. Please enjoy it and share it with anyone that you know who may have known Stephen, or had their musical experience made more alive by using one of his instruments."
Mid Century Electronica from Atomic Shadow on Vimeo.
"A short piece featuring my vintage, tube HP sine wave generators, tape loops and ring modulators with a photographic homage to the early pioneers of electronica.... Daphne Oram in twin set, the impish Delia Derbyshire of the early BBC Radiophonic Workshop, several tweedy boffins in their music labs, Karlheinz Stockhausen and so many others. A different age when innovation and ingenuity triumphed over the many technical limitations of the age.
Abstract music soundtrack re-mixed and produced by Stephen Howell of Hollow Sun using traditional techniques in a digital age."
You can find an interview with Stephen Howell on SoundBytes here.
"I was always huge fan of early electronica and the BBC Radiophonic Workshop (Dr Who, Delia Derbyshire and all that as a six-year-old), Louis and Bebe Barron (who did the ‘electronic tonalities’ for the classic sci-fi movie ‘Forbidden Planet’) and loved the weird old gear they used to make/use, so Mario and I were able to design and create, using Kontakt, weird and wonderful things that flew in the face of, shall we say, more ‘conventional’ modern synths and sampler instruments..."
Indeed. Click here for all posts featuring Hollow Sun on MATRIXSYNTH. Each post is a tribute to his spirit. He will be sorely missed.
Update: Failed Muso has set up a condolence page here.
And on KVR here.
Update2:
Stephen Howell and the Subharchord from Ina Pillat on Vimeo.
"December 2011 at the Museum of Technology (Deutsches Technikmuseum) in Berlin. Stephen Howell takes recordings of the instrument. Per Platou, founder and leader of www.pnek.org, has invited him to create a sound library and helps him with the recordings. Inventor Gerd Steinke in conversation with Stephen Howell.
Photography: Jenny Barth
Sound: Johannes Schmelzer-Ziringer
Director: Ina Pillat
Production: Norwegian Arts Council // Per Platou, Ina Pillat"

Showing posts sorted by date for query Bebe Barron. Sort by relevance Show all posts
Showing posts sorted by date for query Bebe Barron. Sort by relevance Show all posts
Saturday, May 31, 2014
Tuesday, March 25, 2014
O.S.T. Show - London Resonance FM Podcast on the Work of Louis & Bebe Barron
"Originally broadcast on April 27, 2013, the London Resonance FM O.S.T. show with host Jonny Trunk is a fascinating discussion on the Barron's pioneering work in electronic music. This show is now available on SoundCloud. Featured guests on this program include myself and Peter McKerrow. This is a lively, entertaining, and informative discussion on the Barron's music, especially on the score for the film Forbidden Planet."
via Barry Schrader who has an interview on UNDAE Radio from Madrid. Embeds don't work for them, so click through below. Barry also received the 2014 Lifetime Achievement award from SEAMUS. Details below.
"From UNDAE Radio in Madrid comes this two-part broadcast on my music and compositional philosophy. Presented in Spanish and English, these programs are hosted by Antony Maubert, Hertz Volta, and Antonio Sánchez, and are a production of Campo de Interferencias, broadcast on Radio Circulo de Bellas Artes. Recorded live in the radio studio in Madrid, Part 1 was originally broadcast on March 10, 2014, and part 2 on March 17. Included in the broadcasts are several of my works. The podcasts for these shows can also be found here, as UNDÆ! Radio nº 46 and UNDÆ! Radio nº 47."
"I am very pleased to announce that I have been selected to receive the 2014 Lifetime Achievement Award from SEAMUS, The Society for Electro-Acoustic Music in the United States. This award will be presented at the 2014 SEAMUS National Conference at Wesleyan University on Saturday, March 29. On the same evening, at the 8:00 concert in Crowell Hall, the final movement of The Barnum Museum (The Chamber of False Things) will be presented.
Speaking of The Barnum Museum, the CD has received several very positive reviews. Some of the more notable reviews available online can be found at Chain D.L.K., The Computer Music Journal, and Bop-N-Jazz."
Tuesday, March 12, 2013
The Music and SFX of Forbidden Planet
Published on Apr 22, 2012
"Here's an excerpt from Geoff Elliot's tribute documentary about the classic film Forbidden Planet showing Bebe Barron talking about the great music and sfx that she and her husband, Louis, created for the film."
via @Earthnik
"Here's an excerpt from Geoff Elliot's tribute documentary about the classic film Forbidden Planet showing Bebe Barron talking about the great music and sfx that she and her husband, Louis, created for the film."
via @Earthnik
Wednesday, October 17, 2012
Forbidden Planet - Whole Soundtrack Album
Published on Jun 27, 2012 by DaMuzakian
This one in via Connor 'Macleod' Eck on The MATRIXSYNTH Lounge
You can read about the significance of this track and the composer Bebe Barron in this post. Note the film was released in 1956 before the existence of Moog and Buchla modular systems. The first Moog system to be shown was in 1964 and the first Buchla in 1963.
YouTube description:
"Also include scans from the soundtrack album and from the booklets of the "Forbidden Planets" compilations.
amazon.com:
Forbidden Planet: Original MGM Soundtrack
Discogs
In case if anyone's is interested in the "Forbidden Planets" compilations I've mentioned, here are the links:
Tuesday, June 26, 2012
Bleep's Guide to Electronic Music
 This one in via Scott, via Bleep: "Bleep's guide to Electronic Music is a 55 track compilation charting the historical emergence of electronic music by looking at landmark tracks from the 1930s up to present day.
This one in via Scott, via Bleep: "Bleep's guide to Electronic Music is a 55 track compilation charting the historical emergence of electronic music by looking at landmark tracks from the 1930s up to present day.Our aim with this selection of music is to show the length and breadth of the medium, providing a snapshot of the genres forms and styles, and the development of the artform. Whilst there are omissions and compromises that we have had to make, we hope that we achieve our aims and we do some justice to the variety of music that we love.
This compilation developed out of a project to create a Facebook timeline charting the development of electronic music from the late 19th Century until now."
For reference check out 120 Years of Electronic Music
The collection begins with Olivier Messiaen's Oraison from 1937 performed on Ondes Martenot & Theremin (you can find the original full track previously posted here and a beautiful cover on Buchla 200e and Haken Continuum from the late Richard Lainhart here):
"Originally composed by Olivier Messiaen, this beautiful and contemplative piece of music is a monumental moment in electronic music. Argued to be the first piece of purely electronic music written expressly for live performance on the Ondes Martenot, an instrument closely related to the Theremin."
The collection ends with James Blake's CMYK"
"At just 21 years old, London producer, James Blake releases on newly relaunched R&S Records.
At its core 'CMYK' is forged from a myriad of 90's R&B samples (Aaliyah, Kelis) their voices mangled, barely recognisable and thrown into a red-eyed fire of DSP and hours spent in the waveforms."
The full track listing:
Friday, April 08, 2011
Altair-4 The SciFi Sounds Lab DemoVideo
YouTube Uploaded by HGFSynthesizer on Apr 8, 2011
"Altair 4 - The SciFi Sounds Lab
is for spacey & wobbly stuff, drones and scapes i.e SciFi FX-sounds, and it is quite good at doing bell like sounds too.
The movie Forbidden Planet from 1956 being the first movie with a complete electronic soundtrack (by Louis and Bebe Barron) using sounds that could have been done with this plug.
"This instrument does do a lot of the things the Barron's did with their circuitry albeit a lot easier".
"It makes sciFi sounds & noises and everybody will reminiscent to a old soundlaboratory of the 50/60ties".
Anyway Altair 4 puts it to a modern level.
Hence the name of this plugin Altair 4 as this is the Forbidden Planet in the movie ;-)"
Tuesday, December 07, 2010
The Son of Forbidden Planet - mk 04052010
via BB on the Wiard list: "For anyone interested in Forbidden Planet: I made a complete new score on the movie, also using Wiard filters, the noisering and the Wogglebug."
SoundCloud description:
"This is an attempt to make a 2010 version of the score for Forbidden Planet in honour of Louis and Bebe Barron. To keep things spontaneous I made the score from scratch and didn't redo the original score. So, it's A COMPLETELY NEW SCORE. This music is made entirely with the type of soundgenerators and modulators they could use back in 1954. Well at least the same type of technology. I just used analog equipment like noisegenerators, oscillators, lfo's, ring modulators, voltage dividers, tubes, feedback circuits, lab equipment, spring reverbs, tape delay and an occasional sequential switch.
Lucky enough I had Pro tools to put it all together, imagine that Louis and Bebe had to do it all with tape!
In the track i tagged the scenes in the movie, well i tried to, because actually i never saw the movie.
I have the plan to update this piece now and then on irregular base and put up new mixes with of course new scenes added to it.
I was thinking that maybe other people are interested to contribute to this piece. You could send me your files.
However to keep the score original and pure I formulate these rules:
- all sounds has to be electronic
- all sounds has to be analog and made with analog equipment, no digital sounds
- just original electronic sounds, no samples
- give me a name of the scene you contribute
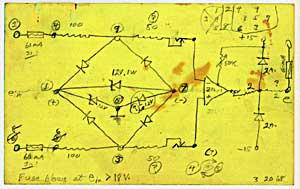
Just to give you an idea, this is how Louis and Bebe worked on their piece:
The 1948 book Cybernetics: Or, Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine, by mathematician Norbert Wiener from MIT played an important role in the development of the Barrons' composition. The science of cybernetics proposes that certain natural laws of behavior apply to both animals and more complex electronic machines.
By following the equations presented in the book, Louis was able to build electronic circuits which he manipulated to generate sounds. Most of the tonalities were generated with a circuit called a ring modulator. The sounds and patterns that came out of the circuits were unique and unpredictable because they were actually overloading the circuits until they burned out to create the sounds. The Barrons could never recreate the same sounds again, though they later tried very hard to recreate their signature sound from Forbidden Planet. Because of the unforeseen life span of the circuitry, the Barrons made a habit of recording everything.
Most of the production was not scripted or notated in any way. The Barrons didn't even consider the process as music composition themselves. The circuit generated sound was not treated as notes, but instead as 'actors'. In future soundtrack composition, each circuit would be manipulated according to actions of the underlying character in the film.
After recording the sounds, the couple manipulated the material by adding effects, such as reverb and tape delay. They also reversed and changed the speed of certain sounds. The mixdown of multiple sounds was performed with at least three tape recorders. The outputs of two machines would be manually synchronized, and fed into an input of a third one, recording two separate sources simultaneously. The synchronization of future film work was accomplished by two 16 mm projectors that were tied into a 16 mm tape recorder, and thus ran at the same speed.
While Louis spent most of his time building the circuits, Bebe did all of the composing. She had to sort through many hours of tape, and as she described it, "it just sounded like dirty noise". Over time, she developed the ability to determine which sounds could become something of interest. She may have invented the tape loop too, as she did not recall ever having heard of it before. The tape loop gave the Barrons' sounds rhythm. Together they mixed the sounds to create the otherworldly and strange electronic soundscapes required by Forbidden Planet.
Finaly: this project is for Mike 'Livewire' Brown, I hope that you get better soon."
Monday, September 28, 2009
A TRIBUTE TO BEBE BARRON by JP
YouTube via stockhausen
"My homage to one of the great 'electronic music' pioneers as in the mid-fifties she and her husband composed and realized the first All-Electronic musical score for the film 'Forbidden Planet'.
Performed by myself on the Arturia Arp 2600v synthesizer.
BEBE BARRON 1925-2008 'there will always be a piece of you within me'-JPVIDEO"
Wednesday, March 04, 2009
Interview With Bebe Barron (Excerpt)
YouTube via takenae
"From OHM+ The Early Gurus Of Electronic Music
Filmed By Barbara Cassidy
Interviewer Eric Chasalow"
You can find OHM in the synth books section on the right.
You can find previous posts featuring Bebe Barron here.
Wednesday, January 28, 2009
Music Non Suck - Early Electronic Music
Radio 216;s Musique Non Suck
Track listing:
01. Raymond Scott - Baltimore Gas & Electric Co. (1960)
02. Laurie Spiegel - Patchwork (1976)
03. Pauline Oliveros - Bye Bye Butterfly (1965)
04. Tom Dissevelt - Ignition (1963)
05. Roger Powell - Lumia (Dance Of The Nebulae) (1973)
06 RCA - demonstration of synthesizing a human voice on the RCA Modular Synthesizer (1955)
07. Ralph Lundsten - IT (1968)
08. Ron Geesin - U.F.O. (1972)
09. Mother Mallard's Portable Masterpiece - Waterwheel (1976)
10. Charles Dodge - discussion on the cumbersomeness of early computer music
11. Charles Dodge - He Destroyed Her Image (1972)
12. Bell Labs - demonstration of the VODER speech synthesizer (1939)
13. Ursula Bogner - Für Ulrich/Pulsation (1969)
14. Erkki Kurenniemi - Sähkösoittimen Ääniä #1 (1971)
15. Gil Mellé - Wildfire (Andromeda Strain Soundtrack) (1971)
16. Delia Derbyshire - Effervescence (1972)
17. Tom Dissevelt - Syncopation (1958)
18. Raymond Scott - IBM Probe (1963)
19. Morton Subotnick - Silver Apples Of The Moon (1967)
20. Hugh Le Caine - demonstration of synthesizing strings on the Electronic Sackbut (1953)
21. Ilhan Mimaroglu - Agony (1965)
22. Raymond Scott - Futurama (1964)
23. Tom Dissevelt - Pacific Dawn (1963)
24. Louis And Bebe Barron - Once Around Altair (Forbidden Planet Soundtrack) (1956)
25. Herbert Eimert And Robert Beyer - Klangstudie II (1952)
26. Erkki Kurenniemi - Improvisaatio (1969)
27. John Pfeiffer - Orders (1968)
28. Frank Coe/Forrest J. Ackerman - Tone Tales From Tomarrow (1964)
via Jez
Saturday, August 02, 2008
Bebe Barron's Mixed Emotions
via Peter Grenader of Plan B:
"In 2000, Curtis Roads, composer, director of the of the electronic music department at UCSB and ex-editor of The Computer Music Journal commissioned his friend Bebe Barron to compose a piece of music at UCSB's CREATE studios.
At first Bebe was hesitant to do this, but at the arguing of Barry Schrader, over a six week period with the technical assistance of composer Jane Brokman, Bebe did in fact compose what was to be her last body of work, aptly entitled 'Mixed Emotions'
Although digital, it has a remarkable analog quality to it, akin to the timbres we would expect from the Barrons. You can hear Bebe speaking about these similarities in a taped audio interview which is still accessible at npr.org (search Barron once on the site, you'll see the link).
Until recently Mixed Emotions was heard only by those who attended it's premier at UCSB and at the 2001 SCREAM Festival at CalArts. Earlier this year however, Leonard Newbauer (Bebe's husband) commissioned a gentleman by the name of Mario Salinas to tape and produce a video of her memorial. In it they included Mixed Emotions, which is accompanied by some really interesting video graphics. The presentation is great. Without hesitation I can say that Bebe would be very pleased.
After some discussion, I have received approval from Leonard to release the Mixed Emotions section of the memorial DVD to the internet. It will be officially premiered on Matrixsynth in the next few days and will take permanent residence on my You Tube space:
http://www.youtube.com/user/petergrenader
Keep your eyes and ears tuned for this significant body of work - the last from legend and first lady of electronic music, Bebe Barron.
- Peter Grenader"
For more info on Bebe Barron's influence and legacy see this post.
Update via Mike in the comments: "And don't forget that Wendy Carlos just posted a lovely tribute to Bebe Barron on her own website: http://www.wendycarlos.com/people/BebeNYC/index.html "
"In 2000, Curtis Roads, composer, director of the of the electronic music department at UCSB and ex-editor of The Computer Music Journal commissioned his friend Bebe Barron to compose a piece of music at UCSB's CREATE studios.
At first Bebe was hesitant to do this, but at the arguing of Barry Schrader, over a six week period with the technical assistance of composer Jane Brokman, Bebe did in fact compose what was to be her last body of work, aptly entitled 'Mixed Emotions'
Although digital, it has a remarkable analog quality to it, akin to the timbres we would expect from the Barrons. You can hear Bebe speaking about these similarities in a taped audio interview which is still accessible at npr.org (search Barron once on the site, you'll see the link).
Until recently Mixed Emotions was heard only by those who attended it's premier at UCSB and at the 2001 SCREAM Festival at CalArts. Earlier this year however, Leonard Newbauer (Bebe's husband) commissioned a gentleman by the name of Mario Salinas to tape and produce a video of her memorial. In it they included Mixed Emotions, which is accompanied by some really interesting video graphics. The presentation is great. Without hesitation I can say that Bebe would be very pleased.
After some discussion, I have received approval from Leonard to release the Mixed Emotions section of the memorial DVD to the internet. It will be officially premiered on Matrixsynth in the next few days and will take permanent residence on my You Tube space:
http://www.youtube.com/user/petergrenader
Keep your eyes and ears tuned for this significant body of work - the last from legend and first lady of electronic music, Bebe Barron.
- Peter Grenader"
For more info on Bebe Barron's influence and legacy see this post.
Update via Mike in the comments: "And don't forget that Wendy Carlos just posted a lovely tribute to Bebe Barron on her own website: http://www.wendycarlos.com/
Monday, April 28, 2008
DELIA DERBYSHIRE- "The Wizards Laboratory" (1972)
YouTube via funknroll
"The Women of ELECTRONIC MUSIC! From the 30's to the 70's!
Before synthesizers, electronic music was honed the hard way in universities, by splicing tape loops, distorting sounds, endless dubbing, and blind instinct. Here are the timeless women of future music who created our present...
Since the 1930's, CLARA ROCKMORE was the master of the notoriously difficult Theremin, and later championed by synthesizer-creator Bob Moog; LOUIS & BEBE BARRON created the first all-electronic score for the film "FORBIDDEN PLANET" (1957), using oscillated sounds and tape loops; //STUDIO d'ASSAI (Paris): Danish ELSE MARIE PADE studied under musique concrete founder Pierre Schaeffer, becoming a noted composer; ELAINE RADIGUE used the Buchla and Arp synthesizers in her work, heavily influenced by Buddhist meditation, and records now with laptop improv group The Lappetites; MICHELE BOKANOWSKI has composed for film, televison, and theatre; //BBC RADIOPHONIC WORKSHOP (London): ...was created and directed by DAPHNE ORAM, inventor and sonic pioneer; she was followed by DELIA DERBYSHIRE, who brought Ron Grainer's "DR. WHO" theme to brilliant, eerie life with her studio wizardry; MADDALENA FAGANDINI co-created the proto-Techno single "Time Beat/ Waltz In Space" (1962) with young producer George Martin under the alias 'Ray Cathode'; GLYNIS JONES produced some of the Workshop's classic albums like "Out Of This World" (1976); ELIZABETH PARKER scored many BBC shows including "BLAKE'S 7", and was the person to see the Workshop out in its 1998 finale; //Fluxus performance artist YOKO ONO expanded John Lennon's mind and range with electronic music, musique concrete, and 'happening' experiments; //COLUMBIA-PRINCETON ELECTRONIC MUSIC CENTER (New York): A premiere focal point for international composers since the 50's, including composer and Associate Director PRIL SMILEY; ALICE SHIELDS combined her operatic voice and poetry with the revolutionary synthesizers of the late 60's and early 70's; teacher DARIA SEMEGEN wrote traditional classical music as well as electronic; WENDY CARLOS had massive mainstream success with the all-synth "Switched On Bach", before writing groundbreaking film scores for "A CLOCKWORK ORANGE," "THE SHINING" and 'TRON"; nearby at Bell Labs, LAURIE SPIEGEL spearheaded computer graphics and software design as well as new music; maverick ANNETTE PEACOCK went from Free Jazz piano to the first synthesizers, threading her early 70's raps and rock with freeform electronics; //Argentinian BEATRIZ FERREYRA, who also studied with Schaeffer, is an esteemed composer and teacher; //SAN FRANCISCO TAPE MUSIC CENTER: The crucial West Coast electronic center, including Morton Subotnick, Terry Riley, Steve Reich and PAULINE OLIVEROS in 1962; it moved across the Bay to become the... //CENTER FOR CONTEMPORARY MUSIC (Mills College, Oakland, CA): Oliveros was the first Director, perfecting her signal processing system for live performance; student and now Co-Director MAGGI PAYNE trailblazed video imagery and record engineering along with her music; alum CYNTHIA WEBSTER played in the early synth band Triode, founded electro mag SYNAPSE, and now runs Cyndustries designing software for electronic music, such as the Zeroscillator.
Their innovations led to Progressiv Rock, Krautrock, New Wave, Coldwave, Darkwave, Electro Funk, Industrial, Techno, and Electroclash. Their fringe future music is now the soundtrack of today.
DELIA DERBYSHIRE: This song is from a 1972 LP called "Ultrasonic", collecting music library pieces Delia scored for use in TV shows. It was recently issued on CD, as was "Oramics" by Daphne Oram:
http://www.boomkat.com/item.cfm?id=89395
http://www.boomkat.com/item.cfm?id=35793
See also:
ALICE SHIELDS -"STUDY FOR VOICE AND TAPE" (1968)
"Sound, the infinite frontier! Science had chopped the world into atoms, components from which to build. Modern art deconstructed reality, reconstructing our perceptions of it. And the first Electronic Music likewise took apart sound and turned it inside out for new compositions. Vladimir Ussachevsky founded the first Electronic Music Center jointly with Columbian and Princeton universities in 1952. He brought in avant composers from countries worldwide with new perspectives and radical expirementation. This included women like Daria Semegen, Pril Smiley, Wendy Carlos, and Alice Shields. In the 50's, Electronic Music was distortions of recordings. Sounds on a tape recorder would be manipulated by feedback, repeated spliced loops, overlapping tracks with multiple recorders, and using oscillators and reverb to sculpt the tempo, tone, or texture. This prevailed in continually advancing ways well through the 1960s. Alice used these techniques in creating this composition. A gifted mezzesoprano, she first sang a poem she'd written. She accompanied this with the first analog Buchla synthesizer, a rare and recent device only beginning to draw the attention of the hippest pop musicians. She then manipulated pitch and speed in textural patterns to supplement the freeform song. This was the cutting edge music of the future, usually heard only in academic circles. But it made its way into film soundtracks (from FORBIDDEN PLANET to Wendy Carlos' A CLOCKWORK ORANGE), Fusion Jazz (Miles Davis, Herbie Hancock), Progressive Rock (from George Harrison's 1969 ELECTRONIC SOUND to Krautrock and Kraftwerk), Funk (Stevie Wonder's T.O.N.T.O., Bernie Worrell), on to the synthesizer explosion of New Wave, then Hip Hop (from Bambaataa's ElectroFunk to Public Enemy's radical sculptures of noise), Industrial (synthetic abrasion), and the Electronica music of today; as such, Alice Shields is a godmother of Le Tigre, Peaches, Chicks On Speed, Lesbians On Ecstasy, and Ladytron, to name a few."
MALARIA! -"Your Turn To Run" (1982)
"The Women of 80's ELECTRO! Coldwave, Darkwave, Synthpop, Industrial!
As synthesizers got smaller and cheaper through the 70's, 'future music' went from acedemia to the street. Punk, PostPunk, Funk, and HipHop artists brought attitude and new styles into the pop vocabulary throughout the 80's that forged the music of today. Here are many women from the first Electro rock era..."
http://www.cyndustries.com/woman.cfm
http://www.newyorkwomencomposers.org/...
http://www.aliceshields.com/
http://www.imtheone.net/annettepeacoc...
http://whitefiles.org/rwg/index.htm"
Sunday, April 20, 2008
RIP Bebe Barron
 via darthmouth (click for the full article)
via darthmouth (click for the full article)"Hollywood, however, had already been utilizing instruments such as the theremin in movie scores for many years, and the first widespread American public exposure to the possibilities of the electronic medium occurred with the 1956 release of MGM's feature film Forbidden Planet. In addition to its elaborate space sets and advanced visual effects, Forbidden Planet featured an exclusively electronic musical score composed by Bebe Barron (b. 1927) and her husband Louis (1920-1989)....
Once they decided on the characters' moods and situations, the couple completed a series of electrical circuits which functioned electronically in ways analogous to the human nervous system. Decisions about the circuitry were strongly influenced by their studies of the science of cybernetics which proposes that certain natural laws of behavior are applicable to both animals and more complex modern machinary. The composers employed their noise-producing circuits to emulate such needed characterizations as serenity, anger, and love....
 Bebe and Louis' success signaled the beginning of the effective use of electroacoustic music by the modern movie industry."
Bebe and Louis' success signaled the beginning of the effective use of electroacoustic music by the modern movie industry."You can also find more on wikipedia.
And of course Google Image search where I found the images for this post.

via Peter Grenader of Plan b:
"We have lost a bright little little light and a dear friend. Bebe Barron has passed. She has captivated us with her charm, her modesty and her enchanting smile and her memory will remain in our hearts, our art and our spiritforever."
Update: some nice words from Barry Schrader:
"Bebe Barron (1925 - 2008)
It is with great sadness that I report the death of Bebe Barron on April 20, 2008 at the age of 82, of natural causes. Bebe was the last of the pioneering composers of classical studio electronic music. She was a close friend, an enthusiastic colleague, and a most gracious lady.
 Bebe Barron was born Charlotte Wind in Minneapolis, on June 16, 1925. She received an MA in political science from the University of Minnesota, where she studied composition with Roque Cordero, and she also spent a year studying composition and ethnomusicology at the University of Mexico. In 1947 she moved to New York and, while working as a researcher for Time-Life, studied composition with Wallingford Reigger and Henry Cowell. That same year, she met and married Louis Barron (1920 - 1989). Shortly thereafter, the Barrons began their experiments with the recording and manipulation of sound material by means of a tape recorder that they received as a wedding gift. They created a private studio in New York and, in 1955, composed the first electronic music score for a commercial film, Forbidden Planet. In 1962 the Barrons moved to Los Angeles; they divorced in 1970. In 1973, Bebe married Leonard Neubauer, a screen writer. Bebe became the first Secretary of the Society for Electro-Acoustic Music in the United States (SEAMUS) in 1985, and also served on the Board of Directors. In 1997 Bebe was presented the SEAMUS Award for the Barrons life work in the field of electro-acoustic music. She is survived by her husband, Leonard, and her son, Adam.
Bebe Barron was born Charlotte Wind in Minneapolis, on June 16, 1925. She received an MA in political science from the University of Minnesota, where she studied composition with Roque Cordero, and she also spent a year studying composition and ethnomusicology at the University of Mexico. In 1947 she moved to New York and, while working as a researcher for Time-Life, studied composition with Wallingford Reigger and Henry Cowell. That same year, she met and married Louis Barron (1920 - 1989). Shortly thereafter, the Barrons began their experiments with the recording and manipulation of sound material by means of a tape recorder that they received as a wedding gift. They created a private studio in New York and, in 1955, composed the first electronic music score for a commercial film, Forbidden Planet. In 1962 the Barrons moved to Los Angeles; they divorced in 1970. In 1973, Bebe married Leonard Neubauer, a screen writer. Bebe became the first Secretary of the Society for Electro-Acoustic Music in the United States (SEAMUS) in 1985, and also served on the Board of Directors. In 1997 Bebe was presented the SEAMUS Award for the Barrons life work in the field of electro-acoustic music. She is survived by her husband, Leonard, and her son, Adam.Bebe’s last public appearance was on January 12, 2008, at an event held at the Hammer Museum in Los Angeles, celebrating the work of her good friend, Anais Nin. Bebe was too ill to speak in public at this point, but she agreed to be interviewed for a video piece that was shown at the event. This is her final interview, and you can see it on YouTube.
Bebe’s final composition, Mixed Emotions (2000) was composed in the CREATE studios of the University of California at Santa Barbara. I'll be putting this work up on the Downloads 2 page of my website, along with some photos of Bebe and myself taken in 2005 at her home on the Photos page within the next week.
 I first met Bebe Barron in the middle 1970s; I don't remember exactly when, but I think it was around 1975. I had asked Bebe and her former husband and composing partner Louis to attend a showing of Forbidden Planet that I had arranged as part of a class at CalArts. They agreed to do it, and I quickly became good friends with Bebe and we remained close over the years.
I first met Bebe Barron in the middle 1970s; I don't remember exactly when, but I think it was around 1975. I had asked Bebe and her former husband and composing partner Louis to attend a showing of Forbidden Planet that I had arranged as part of a class at CalArts. They agreed to do it, and I quickly became good friends with Bebe and we remained close over the years.In writing about Bebe Barron, it's impossible not to focus on the pioneering work that she and Louis did in electronic music. They began their experiments in 1948, shortly after they were married. This early work was done using a tape recorder, preceding the work of Luening and Ussachevsky and the switch from disks to tape by Pierre Schaeffer and the GRM. But, to my knowledge, the Barrons' early experiments did not result in any completed works, a state of affairs not uncommon with early pioneers in the field. In 1949 they set up one of the earliest private electro-acoustic music studios and began their experiments with electronically generated sounds. They built their own circuits which they viewed as cybernetic organisms, having been influenced by Norbert Weiner's work on cybernetics. The circuits, built with vacuum tubes, would exhibit characteristic qualities of pitch, timbre, and rhythm, and had a sort of life cycle from their beginnings until they burned out.
 The Barrons recorded the sounds from the amplification of these circuits and this formed the basis of their working library. They also employed tape manipulation techniques as part of their compositional procedures. The sound qualities of these various amplified tube circuits and the tape manipulations that they underwent formed the musical language that the Barrons created in their studio. Unlike some of the work being done elsewhere, the Barrons' music reveals long phrases, often stated in tape-delayed rhythms, with the stark finesse of the tube circuit timbres. They created a style that was uniquely their own yet married to the technology they were using.
The Barrons recorded the sounds from the amplification of these circuits and this formed the basis of their working library. They also employed tape manipulation techniques as part of their compositional procedures. The sound qualities of these various amplified tube circuits and the tape manipulations that they underwent formed the musical language that the Barrons created in their studio. Unlike some of the work being done elsewhere, the Barrons' music reveals long phrases, often stated in tape-delayed rhythms, with the stark finesse of the tube circuit timbres. They created a style that was uniquely their own yet married to the technology they were using.The Barrons earliest finished work, Heavenly Menagerie (1951) does not seem to have survived in a complete form. But their score for Ian Hugo's film Bells of Atlantis (1952), based on a poem by Anais Nin, who appears on screen, does exist on the film sound track. This may be the earliest extant work of the Barrons and presages what was to come with Forbidden Planet, the music for which was composed in 1955, the film being released the
next year.
 The music for Forbidden Planet is truly a landmark in electro-acoustic music. This was the first commercial film to use only electronic music, and the score for the movie displays an attitude towards film scoring that was different from anything that had happened before. In Forbidden Planet, while there are themes for characters and events in the film, as was traditional in the scoring of that day, the themes are composed and perceived as gestalts, rather than as melodies in traditional movie music. Even more important is the fact that the scoring of Forbidden Planet breaks down the traditional line between music and sound effects since the Barrons' electronic material is used for both. This not only creates a new type of unity in the film sound world, but also allows for a continuum between these two areas that the Barrons exploit in various ways. At some points it's actually impossible to say whether or not what you're hearing is music, sound effect, or both. In doing this, they foreshadowed by decades the now common role of the sound designer in modern film and video.
The music for Forbidden Planet is truly a landmark in electro-acoustic music. This was the first commercial film to use only electronic music, and the score for the movie displays an attitude towards film scoring that was different from anything that had happened before. In Forbidden Planet, while there are themes for characters and events in the film, as was traditional in the scoring of that day, the themes are composed and perceived as gestalts, rather than as melodies in traditional movie music. Even more important is the fact that the scoring of Forbidden Planet breaks down the traditional line between music and sound effects since the Barrons' electronic material is used for both. This not only creates a new type of unity in the film sound world, but also allows for a continuum between these two areas that the Barrons exploit in various ways. At some points it's actually impossible to say whether or not what you're hearing is music, sound effect, or both. In doing this, they foreshadowed by decades the now common role of the sound designer in modern film and video.The Barrons composed many other works for tape, film, and the theater in the 1950s. Their studio became the home for John Cage's Project of Music for Magnetic Tape, and they assisted in the creation of Cage's first chance piece Williams Mix (1951-52), as well as works by other members of the group such as Earle Brown and Morton Feldman. As a studio for the creation of their own and other composers' works, the Barrons' studio served as a functioning center for electro-acoustic music at a time when there was no institutional support of the medium in the United States. It's curious, then, that, for many years, the Barrons, their studio, and their works were largely overlooked by composers and historians in the field. Fortunately, that injustice has since been corrected, and, in 1997, it was my great honor to present to Bebe and, posthumously, to Louis, the SEAMUS Lifetime Achievement Award. Bebe was involved with SEAMUS from the very beginning of the organization. She was one of the ten original members who responded to my organizational call and met at CalArts in November of 1984 to form the group, and she was SEAMUS's first secretary. There may have been a little strong-arming on my part to get her to be involved so actively, but Bebe was always ready to support the cause of electro-acoustic music in whatever way she could.
Bebe created a firm legacy in her music. If the importance of one's work is to be judged in any regard by it's influence, acceptance, longevity, and innovative qualities, then the score for Forbidden Planet is an enormous success. It remains the most widely known electro-acoustic music work on this planet. For me, Bebe Barron will always be the First Lady of electronic music."

Update: BTW, if you have Netflix, you can watch Forbidden Planet online in IE here.
Bebe Barron on Anais Nin Uploaded on Mar 5, 2008
Wednesday, April 16, 2008
Forbidden Synthacon by vgermuse

mp3 here
via vgermuse:
"Here's my little homage to Bebe and Louis Barron's Forbidden Planet. Synthacon a la concrete techniques. Enjoy!"
Saturday, April 14, 2007
The First Synth to....
Update: The new home for this list is now here. You can add to the list there or comment here and I will update both lists. Note that the complete list however will be there as I do not plan on updating this list with updates made there. That would be too much work and would compete with me being able to put up new posts here. Can't let that happen. : ) Related but separate from that list also see https://120years.net. That said...
If you are going to add to the list in the comments, use the same format.
Year - Manufacturer - Model - First at
1837 - C.G. Page (Salem. Mass) - first to produce electronically generated sound (not necessarily associated with a musical instrument). After inventing the Volta in 1800 (an early battery), in 1837 Page was doing experiments with coils and realized when certain coils were attached to a batter they omitted a ringing sound. While he initially thought the ring came from the electrical current was interrupted (battery disconnected), what was actually taking place was the induction through the coils was causing them to vibrate. via Peter Grenader
1885 - Person and Ernst Lorenz -'Elektrisches Musikinstrument' - the first musical instrument designed to produce electrically generated sound. It used electronic vibrations to drive an electromagnet that were connected to resonating boards, which translated these vibrations to sound. via Peter Grenader
1897 - Taddaeus Cahills - Telharmonium - electromechanical instrument.
1936 - Oskar Sala - Mixturtrautonium - first synth using Subharmonic synthesis
1939 - Homer Dudley invents the Parallel Bandpass Vocoder (VODER) - A manually key operated speech synthesizer
1940 - Homer Dudley invents the The Voder speech synthesizer - A device which used the human voice and an artificial voice to produce a composite
Both were researched as a way to transmit speech over copper wires (id est, telephone lines)
1948 - Hugh LeCaine - Electronic Sackbut - First voltage-controlled synthesizer
1948 - Dr. Raymond Scott - Wall of Sound - First polyphonic Sequencing Worstation (electromechanical) and the Electronum - first sequencer.
1950 - CSIR - Mk 1 - The first known use of a digital computer for the purpose playing music
1956 - Louie and Bebe Barron - Produced the first all-electronic musical score for a major motion picture - MGM's 'Forbidden Planet'
1957 - Max V. Mathews at Bell Labs - MUSIC - the first digital synthesizer. Technically, it was a computer program, though it set the stage for every digital synthesizer that proceeded it. See Laurie Spiegel with one here.
1963/64 - Buchla - model 100 modular - 1st "modern" modular synth
1967 - Moog - Moog modular synthesizer I, II & III - 1st commercial modular synth.
1969 - EMS - Synthi VCS-3 - first non-modular mini-synth
1970 - MOOG - Minimoog - 1st Mono Synth with keys (non-modular)
1971 - Tonus/Arp - Soloist - 1st preset mono synth
1971 - John Chowning - developed FM synthesis using the MUSIC-IV language (source), a direct descendent of Mathew's MUSIC program. FM synthesis was later licensed by Yamaha, and used in popular synths such as the DX-7.
1972 - Triadex Muse - first digital synth
""is the first digital musical instrument and was produced in 1972. It was
designed by Edward Fredkin and Marvin Minsky at MIT. It is an algorithmic
music generator: it uses digital logic circuits to produce a sequence of
notes based on the settings of various parameters. It has four small sliders
in that control Volume, Tempo, Pitch, and Fine Pitch. It is not known how
many were made, but they are considered extremely rare.
The Muse is the subject of U. S. Patent 3610801"
1973 - Coupland Digital Music Synthesizer - First Digital (Triadex beat it?) Update via Peter Grenader: "No time to read through all these posts to see if it's come up yet, but the Coupland was vaporwear...it never existed. I met Mark Vail, who's now a friend, by writing him a letter informing him that his story about the Coupland in his Vintage Synthesizers book (GREAT book) which mentioned it's only recorded showing was at the AES show in LA in 1978 was a farce. I was there - at their booth and their suite in the Hilton where the instrument was said to be. I was there on the first day, I was there on the last day. The only thing they had was a small model - about six inches across, sitting on a table. The booth was amazing - this radial orb multiple people could sit in, with a cover that came over each person which played what I remembered was a very impressive demo which swirled around four speakers inside the box. I, and everyone else, were blown away. They kept saying...'it will be here tomorrow, it'll be here tomorrow'...so I showed up the last day just to see it, figuring by the then it would have arrived...it didn't. I did see the frst Synthclavier at that show however. Their suite was across the hall from the Coupland folk. That completely kicked the crap out of everything else shown that year."
1973 - Dartmouth Digital Synthesizer - NED - Synclavier prototype - first digital synth
1974 - Roland - SH-3A - first commercial additive synth
1974 - RMI - Harmonic Synthesizer - first commercial additive synth
1975 - Buchla 502 - six voice polyphonic with minicomputer and ability to save patches to tape drive. Development on the 500 series began in 1969.
1975 - Oberheim FVS - four voice polyphonic with Polyphonic Synthesizer Programmer. Not sure if the Buchla 502 or FVS was released first.
1976 - PPG - PPG 1003 sonic carrier - 1st programmable mono/duo synth with patch memory (this, along with the model 1020, might have been the 1st synths to use DCO's as well)
1977 - Yamaha - CS50/CS60/CS80 - first single enclosure polyphonic keyboard synthesizers with the CS80 to be the first synth with poly aftertouch
1977 (late) - Oberheim - OB-1 - 1st commercial programmable mono synth with patch memory
1978 (late) - PPG - Wavecomputer 360 - 1st wavetable synth
1978 - Sequential Circuits - microprocessor control the SCI prophet 10 (briefly) and the P-5 --- again based on existing E-mu tech stuff
1979 - NED - Synclavier - First FM
1979 - Fairlight CMI - First Sampler, First Workstation
1980 - Performance Music Systems - Syntar - First self contained keytar
1982 - Sequential Circuits - Prophet 600 / First Midi Synthesizer (though some argue the Prophet 5 rev 3.2 is pre-MIDI MIDI)
1983 - Yamaha - DX7 - Digital takes over, FM goes mainstream
1983 - OSC - OSCar - First real-time additive with analog filters
1984 - Sequential Circuits - SixTrak - first multitimbral
1985 - Casio - CZ-101 - First battery-powered all digital mini-synth
1987 - Kawai K5 and Technos Axcel - first additive synths
1989 - E-Mu Systems - Proteus - First dedicated ROMpler
1992 - Seer Systems - first host-based software synthesizer in 1992
1994 - Yamaha - VL1 - first physical modelling synth
1995 - Clavia - Nord Lead - 1st Virtual Analog
1996 - Rubberduck - still not the first softsynth but came before Seer Systems Reality.
1996 - Steinberg - VST - Ok not a synth but enabled a lot to be written as plug-ins and used simultaneously
1997 - Seer Systems - Reality - First Modular Soft Synth
2002 - Hartmann Neuron - first neuronal synth
2912 - KalQuestoTron - the first genetically engineered synth. Each cell is an oscillator, filter, and neural sequencer. Can be delivered via injection to always play 'hold music' in your head.
I thought it might be fun to have a "first synth to..." post. There's been a lot of buzz over Sonic State's Top 20 Synths of All Time with good reason. What exactly is a "top synth?" Is it it's influence on the music scene? It's rarity and lust appeal? The number of synths sold? According to Sonic State their list was the result of Sonic State reader's voting for their favorite synths. Blame the voters if you don't like what you see. Based on what has come up on the list so far, the E-Mu Proteus and Roland JV-1080 for example as well as the Roland Jupiter 8 not even making the top ten, I'm guessing a bit of it has to do with the vote and... possibly the most influential/ground breaking synths for their time. The JV1080 and Proteus? Not super sexy in this day and age, but what they offered in their time? Who knows. It's obviously subjective. But there is something that isn't. The most influential synths of all time not because they were super sexy or utilitarian, but because they offered something that was not previously available.
I thought what might be interesting to create a list of the first synths to feature a particular technology or feature. For example what was the fist synth to bring FM to the table? Was it the DX7 or a predecessor? What was the first digital synth and when? The first additive synth? I have a good idea and could probably look it all up, but that wouldn't be any fun, so.... You tell me. I am going to make this an open post that will live over time. You get to participate by putting an entry in the comments. I will update the list and when I do I will change the time stamp of the post to keep it current. That said, for the archives, this post went up with a time stamp of 4/11/07 7:20 PM PST. I'll start the list (btw, do correct me on the MOOG, what model should we be talking about here? The A, B, C or D or all of them?).
Year - Manufacturer - Model - First at
1970 - MOOG - Minimoog - 1st Mono Synth with keys (non-modular)
1978 - Sequential Circuits - Prophet 5 - 1st Programmable Polyphonic Analog
... List continues above.
Update 3/34/12: Also see the first synthesizers to offer patch storage here.
If you are going to add to the list in the comments, use the same format.
Year - Manufacturer - Model - First at
1837 - C.G. Page (Salem. Mass) - first to produce electronically generated sound (not necessarily associated with a musical instrument). After inventing the Volta in 1800 (an early battery), in 1837 Page was doing experiments with coils and realized when certain coils were attached to a batter they omitted a ringing sound. While he initially thought the ring came from the electrical current was interrupted (battery disconnected), what was actually taking place was the induction through the coils was causing them to vibrate. via Peter Grenader
1885 - Person and Ernst Lorenz -'Elektrisches Musikinstrument' - the first musical instrument designed to produce electrically generated sound. It used electronic vibrations to drive an electromagnet that were connected to resonating boards, which translated these vibrations to sound. via Peter Grenader
1897 - Taddaeus Cahills - Telharmonium - electromechanical instrument.
1936 - Oskar Sala - Mixturtrautonium - first synth using Subharmonic synthesis
1939 - Homer Dudley invents the Parallel Bandpass Vocoder (VODER) - A manually key operated speech synthesizer
1940 - Homer Dudley invents the The Voder speech synthesizer - A device which used the human voice and an artificial voice to produce a composite
Both were researched as a way to transmit speech over copper wires (id est, telephone lines)
1948 - Hugh LeCaine - Electronic Sackbut - First voltage-controlled synthesizer
1948 - Dr. Raymond Scott - Wall of Sound - First polyphonic Sequencing Worstation (electromechanical) and the Electronum - first sequencer.
1950 - CSIR - Mk 1 - The first known use of a digital computer for the purpose playing music
1956 - Louie and Bebe Barron - Produced the first all-electronic musical score for a major motion picture - MGM's 'Forbidden Planet'
1957 - Max V. Mathews at Bell Labs - MUSIC - the first digital synthesizer. Technically, it was a computer program, though it set the stage for every digital synthesizer that proceeded it. See Laurie Spiegel with one here.
1963/64 - Buchla - model 100 modular - 1st "modern" modular synth
1967 - Moog - Moog modular synthesizer I, II & III - 1st commercial modular synth.
1969 - EMS - Synthi VCS-3 - first non-modular mini-synth
1970 - MOOG - Minimoog - 1st Mono Synth with keys (non-modular)
1971 - Tonus/Arp - Soloist - 1st preset mono synth
1971 - John Chowning - developed FM synthesis using the MUSIC-IV language (source), a direct descendent of Mathew's MUSIC program. FM synthesis was later licensed by Yamaha, and used in popular synths such as the DX-7.
1972 - Triadex Muse - first digital synth
""is the first digital musical instrument and was produced in 1972. It was
designed by Edward Fredkin and Marvin Minsky at MIT. It is an algorithmic
music generator: it uses digital logic circuits to produce a sequence of
notes based on the settings of various parameters. It has four small sliders
in that control Volume, Tempo, Pitch, and Fine Pitch. It is not known how
many were made, but they are considered extremely rare.
The Muse is the subject of U. S. Patent 3610801"
1973 - Coupland Digital Music Synthesizer - First Digital (Triadex beat it?) Update via Peter Grenader: "No time to read through all these posts to see if it's come up yet, but the Coupland was vaporwear...it never existed. I met Mark Vail, who's now a friend, by writing him a letter informing him that his story about the Coupland in his Vintage Synthesizers book (GREAT book) which mentioned it's only recorded showing was at the AES show in LA in 1978 was a farce. I was there - at their booth and their suite in the Hilton where the instrument was said to be. I was there on the first day, I was there on the last day. The only thing they had was a small model - about six inches across, sitting on a table. The booth was amazing - this radial orb multiple people could sit in, with a cover that came over each person which played what I remembered was a very impressive demo which swirled around four speakers inside the box. I, and everyone else, were blown away. They kept saying...'it will be here tomorrow, it'll be here tomorrow'...so I showed up the last day just to see it, figuring by the then it would have arrived...it didn't. I did see the frst Synthclavier at that show however. Their suite was across the hall from the Coupland folk. That completely kicked the crap out of everything else shown that year."
1973 - Dartmouth Digital Synthesizer - NED - Synclavier prototype - first digital synth
1974 - Roland - SH-3A - first commercial additive synth
1974 - RMI - Harmonic Synthesizer - first commercial additive synth
1975 - Buchla 502 - six voice polyphonic with minicomputer and ability to save patches to tape drive. Development on the 500 series began in 1969.
1975 - Oberheim FVS - four voice polyphonic with Polyphonic Synthesizer Programmer. Not sure if the Buchla 502 or FVS was released first.
1976 - PPG - PPG 1003 sonic carrier - 1st programmable mono/duo synth with patch memory (this, along with the model 1020, might have been the 1st synths to use DCO's as well)
1977 - Yamaha - CS50/CS60/CS80 - first single enclosure polyphonic keyboard synthesizers with the CS80 to be the first synth with poly aftertouch
1977 (late) - Oberheim - OB-1 - 1st commercial programmable mono synth with patch memory
1978 (late) - PPG - Wavecomputer 360 - 1st wavetable synth
1978 - Sequential Circuits - microprocessor control the SCI prophet 10 (briefly) and the P-5 --- again based on existing E-mu tech stuff
1979 - NED - Synclavier - First FM
1979 - Fairlight CMI - First Sampler, First Workstation
1980 - Performance Music Systems - Syntar - First self contained keytar
1982 - Sequential Circuits - Prophet 600 / First Midi Synthesizer (though some argue the Prophet 5 rev 3.2 is pre-MIDI MIDI)
1983 - Yamaha - DX7 - Digital takes over, FM goes mainstream
1983 - OSC - OSCar - First real-time additive with analog filters
1984 - Sequential Circuits - SixTrak - first multitimbral
1985 - Casio - CZ-101 - First battery-powered all digital mini-synth
1987 - Kawai K5 and Technos Axcel - first additive synths
1989 - E-Mu Systems - Proteus - First dedicated ROMpler
1992 - Seer Systems - first host-based software synthesizer in 1992
1994 - Yamaha - VL1 - first physical modelling synth
1995 - Clavia - Nord Lead - 1st Virtual Analog
1996 - Rubberduck - still not the first softsynth but came before Seer Systems Reality.
1996 - Steinberg - VST - Ok not a synth but enabled a lot to be written as plug-ins and used simultaneously
1997 - Seer Systems - Reality - First Modular Soft Synth
2002 - Hartmann Neuron - first neuronal synth
2912 - KalQuestoTron - the first genetically engineered synth. Each cell is an oscillator, filter, and neural sequencer. Can be delivered via injection to always play 'hold music' in your head.
I thought it might be fun to have a "first synth to..." post. There's been a lot of buzz over Sonic State's Top 20 Synths of All Time with good reason. What exactly is a "top synth?" Is it it's influence on the music scene? It's rarity and lust appeal? The number of synths sold? According to Sonic State their list was the result of Sonic State reader's voting for their favorite synths. Blame the voters if you don't like what you see. Based on what has come up on the list so far, the E-Mu Proteus and Roland JV-1080 for example as well as the Roland Jupiter 8 not even making the top ten, I'm guessing a bit of it has to do with the vote and... possibly the most influential/ground breaking synths for their time. The JV1080 and Proteus? Not super sexy in this day and age, but what they offered in their time? Who knows. It's obviously subjective. But there is something that isn't. The most influential synths of all time not because they were super sexy or utilitarian, but because they offered something that was not previously available.
I thought what might be interesting to create a list of the first synths to feature a particular technology or feature. For example what was the fist synth to bring FM to the table? Was it the DX7 or a predecessor? What was the first digital synth and when? The first additive synth? I have a good idea and could probably look it all up, but that wouldn't be any fun, so.... You tell me. I am going to make this an open post that will live over time. You get to participate by putting an entry in the comments. I will update the list and when I do I will change the time stamp of the post to keep it current. That said, for the archives, this post went up with a time stamp of 4/11/07 7:20 PM PST. I'll start the list (btw, do correct me on the MOOG, what model should we be talking about here? The A, B, C or D or all of them?).
Year - Manufacturer - Model - First at
1970 - MOOG - Minimoog - 1st Mono Synth with keys (non-modular)
1978 - Sequential Circuits - Prophet 5 - 1st Programmable Polyphonic Analog
... List continues above.
Update 3/34/12: Also see the first synthesizers to offer patch storage here.
PREVIOUS PAGE
HOME












© Matrixsynth - All posts are presented here for informative, historical and educative purposes as applicable within fair use.
MATRIXSYNTH is supported by affiliate links that use cookies to track clickthroughs and sales. See the privacy policy for details.
MATRIXSYNTH - EVERYTHING SYNTH













© Matrixsynth - All posts are presented here for informative, historical and educative purposes as applicable within fair use.
MATRIXSYNTH is supported by affiliate links that use cookies to track clickthroughs and sales. See the privacy policy for details.
MATRIXSYNTH - EVERYTHING SYNTH