Showing posts sorted by relevance for query PIERRE SCHAEFFER. Sort by date Show all posts
Showing posts sorted by relevance for query PIERRE SCHAEFFER. Sort by date Show all posts
Wednesday, June 01, 2022
Envelop the Waves
video upload by MAKEN0ISE
"The envelope is a container. It’s the thing you place the message in before you send it. The envelope of a sound is its shape, or as Pierre Schaeffer called it, the “profile.”
In a modular synth, you can use an envelope to "envelop" any kind of sound, including one that already has its own envelope or profile!
Born and raised in New York, Anthony Baldino is an LA based composer and sound designer whose work spans an enormous range of production avenues. The likelihood that you haven't heard his work is nearly impossible, with music and sound design in too many trailer campaigns to list, including Tenet, Prometheus, Interstellar, Ex-Machina, Star Wars: Rogue One, and Avengers: Infinity War and End Game just to name a few. From there, his work ventures to the opposite pole of production with custom sound design based compositions for Dolby Labs mixed in Atmos, beautifully glitched out remixes, and continues on to mind-bending modular synthesizer performances.
Download Anthony's Morphagene Reel here: https://freesound.org/people/makenois...
Anthony's latest release:
https://anthonybaldino.bandcamp.com/a..."
http://www.makenoisemusic.com
Friday, March 02, 2007
Introduction to Electro-Acoustic Music
 I added another book to the list of Synth Books to the right. This one is via Barry Schroder, featured in these previous posts. The book is out of print, however you can find copies here.
I added another book to the list of Synth Books to the right. This one is via Barry Schroder, featured in these previous posts. The book is out of print, however you can find copies here.Details pulled from here:
"This book presents a detailed panorama of electroacoustic music’s principal trends. His approach includes general ideas (terminology, role, listening experience), interviews with several important composers, instruments and devices, the principal historical and current techniques and the studios. Each element includes numerous examples of musical works.
Table of contents:
1. Introduction
2. Musique concrète and tape manipulation techniques
- Pierre Schaeffer and the Études of 1948
- Tape loops
- Cutting and splicing
- Speed change
- Direction change
- Tape delay
- Combined tape and manipulation techniques
3. Electronic music
- Electro-acoustic musical instruments
- Electronic music and optical sound tracks
- Classical studio electronic music: the Cologne studio and its precursors
- Classical studio electronic music: the development of classical studio
- Electronic music synthesizers
- Computer music
- Live/electronic music
4. The art of electro-acoustic Music: interviews with composers
- Interview with Luciano Berio (Thema: Omaggio a Joyce)
- Interview with Pauline Oliveros (I of IV)
- Interview with Morton Subotnick (Until Spring)
- Interview with Jean-Claude Risset (Mutations I)
- Interview with Gordon Mumma (Cybersonic Cantilevers)
5. Bibliography"
Friday, October 23, 2015
What is Krell? Louis & Bebe Barron - Ancient Krell Music (Forbidden Planet) & More
video upload by SoundtracksForLiving
You'll often see videos with references to "Krell" patches. Where did the reference come from? The 1956 film Forbidden Planet and specifically the sounds created for it by Bebe and Louis Barron. The Krell was the intelligent alien race in the film. The above is a playlist I found of various Krell style compositions starting with "Louis & Bebe Barron - Ancient Krell Music." The actual style of composition is considered Musique Concrete which began in the 1940s, much earlier than the film.
"Musique concrète (French pronunciation: [myzik kɔ̃.kʁɛt], meaning 'concrete music') is a genre of electroacoustic music that is made in part from acousmatic sound, or sound without an apparent originating cause. It can feature sounds derived from recordings of musical instruments, the human voice, and the natural environment as well as those created using synthesizers and computer-based digital signal processing. Compositions in this idiom are not restricted to the normal musical rules of melody, harmony, rhythm, metre, and so on. Originally contrasted with 'pure' elektronische Musik (based solely on the production and manipulation of electronically produced sounds rather than recorded sounds), the theoretical basis of musique concrète as a compositional practice was developed by Pierre Schaeffer, beginning in the early 1940s."
And on the soundtrack for Forbidden Planet via Wikipedia:
"Forbidden Planet 's innovative electronic music score, credited as 'electronic tonalities,' partly to avoid having to pay any of the film industry music guild fees,[citation needed] was composed by Bebe and Louis Barron. MGM producer Dore Schary discovered the couple quite by chance at a beatnik nightclub in Greenwich Village while on a family Christmas visit to New York City; Schary hired them on the spot to compose his film's musical score. While the theremin (which was not used in Forbidden Planet) had been used on the soundtrack of Alfred Hitchcock's Spellbound (1945), the Barrons' electronic composition is credited with being the first completely electronic film score; their soundtrack preceded the invention of the Moog synthesizer by eight years (1964).
Using ideas and procedures from the book, Cybernetics: Or, Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine (1948) by the mathematician and electrical engineer Norbert Wiener, Louis Barron constructed his own electronic circuits that he used to generate the score's 'bleeps, blurps, whirs, whines, throbs, hums, and screeches'.[12] Most of these sounds were generated using an electronic circuit called a 'ring modulator'. After recording the basic sounds, the Barrons further manipulated the sounds by adding other effects, such as reverberation and delay, and reversing or changing the speeds of certain sounds.[21]
Since Bebe and Louis Barron did not belong to the Musicians Union, their work could not be considered for an Academy Award, in either the 'soundtrack' or the 'sound effects' categories. MGM declined to publish a soundtrack album at the same time that Forbidden Planet was released. However, film composer and conductor David Rose later published a 7" (18 cm) single of his original main title theme that he had recorded at the MGM Studios in Culver City during March 1956. His main title theme had been discarded when Rose, who had originally been hired to compose the musical score in 1955, was discharged from the project by Dore Schary sometime between Christmas 1955 and New Year’s Day. The film's original theatrical trailer contains snippets of Rose's score, the tapes of which Rose reportedly later destroyed.[22]
The Barrons finally released their soundtrack in 1976 as an LP album for the film's 20th anniversary; it was on their very own Planet Records label (later changed to Small Planet Records and distributed by GNP Crescendo Records). The LP was premiered at MidAmeriCon, the 34th World Science Fiction Convention, held in Kansas City, MO over the 1976 Labor Day weekend, as part of a 20th Anniversary celebration of Forbidden Planet held at that Worldcon; the Barrons were there promoting their album's first release, signing all the copies sold at the convention. They also introduced the first of three packed-house screenings that showed an MGM 35mm fine grain vault print in original CinemaScope and stereophonic sound. A decade later, in 1986, their soundtrack was released on a music CD for the film's 30th Anniversary, with a six-page color booklet containing images from Forbidden Planet, plus liner notes from the composers, Bebe and Louis Barron, and Bill Malone.[21]"
So now when you see a Krell patch posted here on MATRIXSYNTH, you'll know exactly where the reference came from; Bebe & Louis Barron, in 1956, for the film Forbidden Planet.
Friday, May 13, 2016
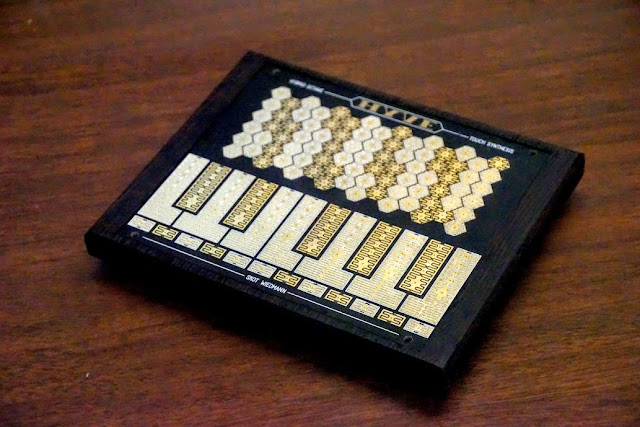
Upcoming Hyve Touch Synthesizer ElectroSound Exhibit in Paris
The Hyve Touch Synthesizer will be at the ElectroSound Exhibit in Paris May 25 to 2 October 2016. You'll find the ElectroSound site in French here and Googlish here.
via Skot Weidmann, creator of the Hyve Touch Synthesizer and the man behind Motus Mavis:
"I am so excited to be a part of the ElectroSound exhibit in Paris.
The Hyve Touch Synthesizer will be included in the Future section of the show, and visitors will get to play it!"
We have Skot to thank for bringing the event to our attention!
Exhibits will also include (apologies for the translations via Google):
Pictured: Daphne Oram
"Jean-Yves Leloup and NoDesign, the commissioners Electrosound, chose a unique perspective to talk about, with the red wire machines and technological innovation. They plunge us into an immersive, interactive experience scanning a wide spectrum of musical productions, from 1945 to today, pioneers and scientists from 1950 to 1970 (Pierre Schaeffer, Robert Moog, Peter Zinoviev, Brian Eno, Jean-Michel Jarre ...) to the current and popular triumph electro. Electrosound, the lab at the dancefloor going back in time, over the 20th century that saw the electricity and electronics invest the musical field, until emergence of a major cultural movement, which is called 'electro', 'house' or 'techno'."
"Electrosound, the lab at the dancefloor, is an exhibition aimed at a wide audience, the curious beginner to the connoisseur. It is divided into six chapters decrypting the major stages of this musical revolution. Around a timeline, she meets machines and period instruments (synthesizers, drum machines, and other strange machines), popular objects of broadcasting and listening to music, archives (from the GRM, EMS studios and many international sources) and artistic photographs by Jean-Jacques or Jacob Ader Khrist, showing changes since search studios 1950s until the DJ culture."
LABELS/MORE:
ElectroSound Exhibit,
EMS,
events,
MOTUS MAVIS,
Oramics,
Skot Wiedmann,
Synth Chicks,
synth museums
Monday, March 19, 2012
Live at the Graham Foundation, Madlener House, Chicago, IL, March 10th, 2012 ; presented by Lampo.
Update: the original video for this post (via kwf on Vimeo) appears to have been removed from Vimeo. Above is a playlist of the event from seijinlee on YouTube.
"KEITH FULLERTON WHITMAN
SAT MAR 10 8pm
Graham Foundation
Madlener House
4 West Burton Place
At long last, Keith Fullerton Whitman makes his Lampo debut. To mark the special occasion, he offers the U.S. premiere of "Rhythmes Naturels," created at the legendary INA-GRM studios, plus a live modular synth improvisation.
Alors, last October Whitman spent a week in Paris, commissioned to develop a new piece for François Bayle's Acousmonium, an 80-speaker sound system designed in 1974 for the Groupe de Recherches Musicales. Pierre Schaeffer formed GRM, a studio and collective, in the late 1950s to encourage the development of electronic music. Members included Luc Ferrari, Iannis Xenakis, Bernard Parmegiani, among other lions; in the late 1960s Bayle became its director. For a whelp like Keith, the residency was "a life-long dream come true." And, he says, "The piece turned out exactly as I hoped."
Here, he'll do his new work in a 4-channel mix. Here, he talks about the residency, etc.
Keith Fullerton Whitman (b. 1973, Bergen County, N.J.) is a composer and performer obsessed with electronic music, from its mid-century origins in Europe to its contemporary worldwide incarnation as digital music. Currently he is working towards implementing a complete system for live performance of improvised electronic music, which incorporates elements from nearly every era. He has recorded albums influenced by many genres, including ambient music, drone, drill and bass, musique concrète and krautrock. He has recorded and performed using several aliases, of which the most familiar is Hrvatski. Today most of his work is recorded under his real name. Whitman lives in Cambridge, Massachusetts."
Sunday, December 19, 2021
The Gmebaphone Concept and the Cybernéphone Instrument
This one is in via Asbjørn Blokkum Flø. "Here is an interesting synth produced in various forms from 1973-2001. It was produced in various analogue and digital forms. If you do a Google image search for 'Gmebaphone' you will see a few different versions. The music of Christian Clozier and Françoise Barrière probably includes the instrument. I tried the instrument at the Bourges festival in 2004, and it was quirky but fascinating."
via https://ur.booksc.eu/book/43779232/b24219
"The Gmebaphone is an instrumentarium consisting of amplifiers, sound-treatment systems, loudspeakers, a console, and a processing system designed and built for live diffusion and performance. The specifications for the instrument were dictated by musical criteria. The musical interpretation of a work is based on analysis of the work and on analysis of its physical signals. Thus, the instrument is able to provide a pertinent acoustic rendering of a work’s sonic complexities (in terms of timbre, time, and space) directly under the performer’s control, thereby allowing transparent and expressive interpretations. The Gmebaphone is a processor/simulator of sonic electroacoustic space, as well as a polyphonic acoustic synthesizer of musical spaces. It is an instrument comprised of the hierarchical combination of a control system with memory, tablatures, and combinatory modes of play that give rise to a rich and workable system of interpretation and expression."
Also see https://collectionsdumusee.philharmoniedeparis.fr/
Image below with an E-Mu Modular in the back ground, and EMS Putney on the left via here. Not sure what the black system on the farl left is. If you know feel free to leave a comment. Also if you know if any demos of the Gmebaphone let us know!
P.S. The design reminds me of various equipment featured in synth rorschach posts.
See the exclusive label for more of the rare of the rare in the synth world.
Update: additonal info in via Asbjørn Blokkum Flø:
I've looked further into the Gmebaphone.
It basically looks like a system for live surround sound for electronic music, or as it is called "diffusion" of electroacoustic music. The surround setups could be very complex with up to 50 loudspeakers of various shapes and placements, a bit like the Acousmonium (GRM 1974-) [link]
The term 'acoustic' is used several times in the article. This seems to describe how loudspeakers interacts with the acoustics of the space, and not acoustic sound sources in the traditional meaning the word.
Being built as a custom instrument for live performance of electronic music, it is more of a musical and compositional tool than a conventional analogue or digital mixer.
It evolved over the years, but the latest model seemed to have a 76 channel mixer with 8 inputs and 16 outputs, with the possibility of digital treatments (phasing, delay, reverberation, and detuning).
From the article:
'The console has a total number of 76 channels of diffusion (36 are touch-controlled and 40 are digitally controlled via the screens) spread over 16 master outputs and eight master inputs. [..] Pull-down menus control digital treatments (phasing, delay, reverberation, and detuning).'
The article describes 6 different models (with photos):
Gmebaphone 1 (1973)
Gmebaphone 2 (1975) - 6 inputs, 2 "networks" (outputs?).
Gmebaphone 3 (1979) - 8 inputs, 22 outputs. Manual analogue control as well as digital computer control.
Gmebaphone 4 (1983) - Digital playback of soundfiles. Digital treatments (phasing, delay, and timbre).
Gmebaphone 5 (1992) - sequencing, graphical interface, automation.
Gmebaphone 6 - (renamed Cybernéphone) (1997) - 8 inputs, 16 outputs, 50 loudspeakers. Possible to save files to CD-ROM.
This page mentions the Gmebaphone number 7 / Cybernéphone (2005): [link]
The convoluted language of the article reminds me of the writings of French composer Pierre Schaeffer, and can be a bit hard to decipher.
--------
There is also some information on a large number of synthesizers that they produced between 1973 and 2008. called Systhysysop (1976), Charybde (1985), Gmebogosse (1972-1999) and Cybersongosse (??-2008?).
They are described in this article (with images): [link]
Many nice images here: [pdf link]
Another article: [link]
More images: [link 1 Also captured here] [link 2] [link 3 Also captured here]
These instruments was also made at the International Institute of Electroacoustic Music at Bourges /IMEB. Read more about IMEB here (use Google translate). [link]
You have written about the Cybersongosse before: [link]
I could not find any audio clips.
All the best"
Sunday, December 01, 2013
Halim El-Dabh - Pest Control, Tape Manipulation & The RCA Synthesizer
Astronauta Pinguim has published yet another interview with one of the pioneers of electronic music. This time around we have an interview with Halim El-Dabh (Portuguese version here). It is a fascinating read. He was the first person to create a musical composition using tape manipulation, and the source of his inspiration came from his work in agriculture.
"'My first exposure to electronic sound devices was back in 1943. As an agriculturist studying pest control, I wanted to see if sound-emitting devices could control tiny beetles that attack wheat, corn, alfalfa and beans. I thought that rather than getting rid of the beetles, we could distract them. I used to experiment with clanging together iron rods like bells; then I tried scratching the rods together to see if it discouraged the bugs.'"
"In 1944 Halim decided to record the ceremony of the Zaar (a female religious ceremony), he then treated the recordings he made on the ceremony using studio techniques and electronic devices and voilà, the first piece of tape manipulation in the world was born! (Note that it happened four years before Pierre Schaeffer released his first published works in France). The Expression Of The Zaar was Halim's only piece to be published from this period, but he created another pieces of tape manipulation mostly of street vendors in Cairo."
In essence, this was the birth of musique concrete.
On The RCA Synthesizer: "'The synthesizer was an innovation that gave us a larger expansion of sound manipulation. We used punch cards to input and receive sound from the machine. It took up a whole wall, it was huge. We were able to get very clear sounds of whatever we synthesized whether it was trumpet, violin or any other sound. I especially liked to input my voice. Luening did an input of his piccolo to transform it. I did an input of my drum to transform it and then took the sounds back from the synthesizer.'"
Be sure to read the full interview on Astronauta Pinguim here. You can find links to additional interviews on Astronauta Pinguim here.
via Fabricio Carvalho aka Astronauta Pinguim on The MATRIXSYNTH Lounge
"'My first exposure to electronic sound devices was back in 1943. As an agriculturist studying pest control, I wanted to see if sound-emitting devices could control tiny beetles that attack wheat, corn, alfalfa and beans. I thought that rather than getting rid of the beetles, we could distract them. I used to experiment with clanging together iron rods like bells; then I tried scratching the rods together to see if it discouraged the bugs.'"
"In 1944 Halim decided to record the ceremony of the Zaar (a female religious ceremony), he then treated the recordings he made on the ceremony using studio techniques and electronic devices and voilà, the first piece of tape manipulation in the world was born! (Note that it happened four years before Pierre Schaeffer released his first published works in France). The Expression Of The Zaar was Halim's only piece to be published from this period, but he created another pieces of tape manipulation mostly of street vendors in Cairo."
In essence, this was the birth of musique concrete.
On The RCA Synthesizer: "'The synthesizer was an innovation that gave us a larger expansion of sound manipulation. We used punch cards to input and receive sound from the machine. It took up a whole wall, it was huge. We were able to get very clear sounds of whatever we synthesized whether it was trumpet, violin or any other sound. I especially liked to input my voice. Luening did an input of his piccolo to transform it. I did an input of my drum to transform it and then took the sounds back from the synthesizer.'"
Be sure to read the full interview on Astronauta Pinguim here. You can find links to additional interviews on Astronauta Pinguim here.
via Fabricio Carvalho aka Astronauta Pinguim on The MATRIXSYNTH Lounge
Wednesday, August 24, 2005
Electronic Composer Luc Ferrari Passes Away
Via Create Digital Music. Click through title for more.
"Paris-born composer Luc Ferrari was a pioneer both of electronic and instrumental avant-garde music. He was the founding director of the Groupe de Musique Concrète in 1958 and was, along with Pierre Schaeffer, one of its leading practitioners. As a documentary producer, he profiled composers from Varèse to Cecil Taylor. He continued as an active composer, teacher/lecturer, and "sound hunter" throughout his life."
"Paris-born composer Luc Ferrari was a pioneer both of electronic and instrumental avant-garde music. He was the founding director of the Groupe de Musique Concrète in 1958 and was, along with Pierre Schaeffer, one of its leading practitioners. As a documentary producer, he profiled composers from Varèse to Cecil Taylor. He continued as an active composer, teacher/lecturer, and "sound hunter" throughout his life."
Sunday, January 20, 2008
JMJ Faux Pas
Some of you might have known that in this Sunday's UK Newspaper 'The Mail On Sunday' Jean Michel Jarre's Oxygene was given out for free with the price of the paper. Apparently the liner notes are as follows:
"Original score re-recorded (sic) and mixed by Jean Michel Jarre at JMJ Studio in High Definition 24 bits/96KHZ. "This album is dedicated to the following people without whom OXYGENE would never have existed: Pierre Schaeffer, who taught me everything in electro- acoustic and electronic music, Peter Zinovieff, who conceived the first European synthesizer and my first one, the VCS3, the Dutch company, Eminent, who built the fantastic string ensemble Eminent 310, Alan R. Pearlman, who created the ARP 2600 and 2500, Les Bradley, who developed the Mellotron, Ikutaro Kakehashi, founder of Roland , who gave us the Minipop (sic) and so many other marvels, Mike Matthews, who imagined these crazy pedals such as the Small Stone and the Electric Mistress, and my friend Robert Moog for obvious reasons."
Yep... That would be KORG that brought us the Minipops. If anyone can confirm this please do. This one via Benjamin Ward on the AH list.
"Original score re-recorded (sic) and mixed by Jean Michel Jarre at JMJ Studio in High Definition 24 bits/96KHZ. "This album is dedicated to the following people without whom OXYGENE would never have existed: Pierre Schaeffer, who taught me everything in electro- acoustic and electronic music, Peter Zinovieff, who conceived the first European synthesizer and my first one, the VCS3, the Dutch company, Eminent, who built the fantastic string ensemble Eminent 310, Alan R. Pearlman, who created the ARP 2600 and 2500, Les Bradley, who developed the Mellotron, Ikutaro Kakehashi, founder of Roland , who gave us the Minipop (sic) and so many other marvels, Mike Matthews, who imagined these crazy pedals such as the Small Stone and the Electric Mistress, and my friend Robert Moog for obvious reasons."
Yep... That would be KORG that brought us the Minipops. If anyone can confirm this please do. This one via Benjamin Ward on the AH list.
Sunday, April 20, 2008
RIP Bebe Barron
 via darthmouth (click for the full article)
via darthmouth (click for the full article)"Hollywood, however, had already been utilizing instruments such as the theremin in movie scores for many years, and the first widespread American public exposure to the possibilities of the electronic medium occurred with the 1956 release of MGM's feature film Forbidden Planet. In addition to its elaborate space sets and advanced visual effects, Forbidden Planet featured an exclusively electronic musical score composed by Bebe Barron (b. 1927) and her husband Louis (1920-1989)....
Once they decided on the characters' moods and situations, the couple completed a series of electrical circuits which functioned electronically in ways analogous to the human nervous system. Decisions about the circuitry were strongly influenced by their studies of the science of cybernetics which proposes that certain natural laws of behavior are applicable to both animals and more complex modern machinary. The composers employed their noise-producing circuits to emulate such needed characterizations as serenity, anger, and love....
 Bebe and Louis' success signaled the beginning of the effective use of electroacoustic music by the modern movie industry."
Bebe and Louis' success signaled the beginning of the effective use of electroacoustic music by the modern movie industry."You can also find more on wikipedia.
And of course Google Image search where I found the images for this post.

via Peter Grenader of Plan b:
"We have lost a bright little little light and a dear friend. Bebe Barron has passed. She has captivated us with her charm, her modesty and her enchanting smile and her memory will remain in our hearts, our art and our spiritforever."
Update: some nice words from Barry Schrader:
"Bebe Barron (1925 - 2008)
It is with great sadness that I report the death of Bebe Barron on April 20, 2008 at the age of 82, of natural causes. Bebe was the last of the pioneering composers of classical studio electronic music. She was a close friend, an enthusiastic colleague, and a most gracious lady.
 Bebe Barron was born Charlotte Wind in Minneapolis, on June 16, 1925. She received an MA in political science from the University of Minnesota, where she studied composition with Roque Cordero, and she also spent a year studying composition and ethnomusicology at the University of Mexico. In 1947 she moved to New York and, while working as a researcher for Time-Life, studied composition with Wallingford Reigger and Henry Cowell. That same year, she met and married Louis Barron (1920 - 1989). Shortly thereafter, the Barrons began their experiments with the recording and manipulation of sound material by means of a tape recorder that they received as a wedding gift. They created a private studio in New York and, in 1955, composed the first electronic music score for a commercial film, Forbidden Planet. In 1962 the Barrons moved to Los Angeles; they divorced in 1970. In 1973, Bebe married Leonard Neubauer, a screen writer. Bebe became the first Secretary of the Society for Electro-Acoustic Music in the United States (SEAMUS) in 1985, and also served on the Board of Directors. In 1997 Bebe was presented the SEAMUS Award for the Barrons life work in the field of electro-acoustic music. She is survived by her husband, Leonard, and her son, Adam.
Bebe Barron was born Charlotte Wind in Minneapolis, on June 16, 1925. She received an MA in political science from the University of Minnesota, where she studied composition with Roque Cordero, and she also spent a year studying composition and ethnomusicology at the University of Mexico. In 1947 she moved to New York and, while working as a researcher for Time-Life, studied composition with Wallingford Reigger and Henry Cowell. That same year, she met and married Louis Barron (1920 - 1989). Shortly thereafter, the Barrons began their experiments with the recording and manipulation of sound material by means of a tape recorder that they received as a wedding gift. They created a private studio in New York and, in 1955, composed the first electronic music score for a commercial film, Forbidden Planet. In 1962 the Barrons moved to Los Angeles; they divorced in 1970. In 1973, Bebe married Leonard Neubauer, a screen writer. Bebe became the first Secretary of the Society for Electro-Acoustic Music in the United States (SEAMUS) in 1985, and also served on the Board of Directors. In 1997 Bebe was presented the SEAMUS Award for the Barrons life work in the field of electro-acoustic music. She is survived by her husband, Leonard, and her son, Adam.Bebe’s last public appearance was on January 12, 2008, at an event held at the Hammer Museum in Los Angeles, celebrating the work of her good friend, Anais Nin. Bebe was too ill to speak in public at this point, but she agreed to be interviewed for a video piece that was shown at the event. This is her final interview, and you can see it on YouTube.
Bebe’s final composition, Mixed Emotions (2000) was composed in the CREATE studios of the University of California at Santa Barbara. I'll be putting this work up on the Downloads 2 page of my website, along with some photos of Bebe and myself taken in 2005 at her home on the Photos page within the next week.
 I first met Bebe Barron in the middle 1970s; I don't remember exactly when, but I think it was around 1975. I had asked Bebe and her former husband and composing partner Louis to attend a showing of Forbidden Planet that I had arranged as part of a class at CalArts. They agreed to do it, and I quickly became good friends with Bebe and we remained close over the years.
I first met Bebe Barron in the middle 1970s; I don't remember exactly when, but I think it was around 1975. I had asked Bebe and her former husband and composing partner Louis to attend a showing of Forbidden Planet that I had arranged as part of a class at CalArts. They agreed to do it, and I quickly became good friends with Bebe and we remained close over the years.In writing about Bebe Barron, it's impossible not to focus on the pioneering work that she and Louis did in electronic music. They began their experiments in 1948, shortly after they were married. This early work was done using a tape recorder, preceding the work of Luening and Ussachevsky and the switch from disks to tape by Pierre Schaeffer and the GRM. But, to my knowledge, the Barrons' early experiments did not result in any completed works, a state of affairs not uncommon with early pioneers in the field. In 1949 they set up one of the earliest private electro-acoustic music studios and began their experiments with electronically generated sounds. They built their own circuits which they viewed as cybernetic organisms, having been influenced by Norbert Weiner's work on cybernetics. The circuits, built with vacuum tubes, would exhibit characteristic qualities of pitch, timbre, and rhythm, and had a sort of life cycle from their beginnings until they burned out.
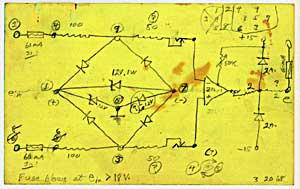 The Barrons recorded the sounds from the amplification of these circuits and this formed the basis of their working library. They also employed tape manipulation techniques as part of their compositional procedures. The sound qualities of these various amplified tube circuits and the tape manipulations that they underwent formed the musical language that the Barrons created in their studio. Unlike some of the work being done elsewhere, the Barrons' music reveals long phrases, often stated in tape-delayed rhythms, with the stark finesse of the tube circuit timbres. They created a style that was uniquely their own yet married to the technology they were using.
The Barrons recorded the sounds from the amplification of these circuits and this formed the basis of their working library. They also employed tape manipulation techniques as part of their compositional procedures. The sound qualities of these various amplified tube circuits and the tape manipulations that they underwent formed the musical language that the Barrons created in their studio. Unlike some of the work being done elsewhere, the Barrons' music reveals long phrases, often stated in tape-delayed rhythms, with the stark finesse of the tube circuit timbres. They created a style that was uniquely their own yet married to the technology they were using.The Barrons earliest finished work, Heavenly Menagerie (1951) does not seem to have survived in a complete form. But their score for Ian Hugo's film Bells of Atlantis (1952), based on a poem by Anais Nin, who appears on screen, does exist on the film sound track. This may be the earliest extant work of the Barrons and presages what was to come with Forbidden Planet, the music for which was composed in 1955, the film being released the
next year.
 The music for Forbidden Planet is truly a landmark in electro-acoustic music. This was the first commercial film to use only electronic music, and the score for the movie displays an attitude towards film scoring that was different from anything that had happened before. In Forbidden Planet, while there are themes for characters and events in the film, as was traditional in the scoring of that day, the themes are composed and perceived as gestalts, rather than as melodies in traditional movie music. Even more important is the fact that the scoring of Forbidden Planet breaks down the traditional line between music and sound effects since the Barrons' electronic material is used for both. This not only creates a new type of unity in the film sound world, but also allows for a continuum between these two areas that the Barrons exploit in various ways. At some points it's actually impossible to say whether or not what you're hearing is music, sound effect, or both. In doing this, they foreshadowed by decades the now common role of the sound designer in modern film and video.
The music for Forbidden Planet is truly a landmark in electro-acoustic music. This was the first commercial film to use only electronic music, and the score for the movie displays an attitude towards film scoring that was different from anything that had happened before. In Forbidden Planet, while there are themes for characters and events in the film, as was traditional in the scoring of that day, the themes are composed and perceived as gestalts, rather than as melodies in traditional movie music. Even more important is the fact that the scoring of Forbidden Planet breaks down the traditional line between music and sound effects since the Barrons' electronic material is used for both. This not only creates a new type of unity in the film sound world, but also allows for a continuum between these two areas that the Barrons exploit in various ways. At some points it's actually impossible to say whether or not what you're hearing is music, sound effect, or both. In doing this, they foreshadowed by decades the now common role of the sound designer in modern film and video.The Barrons composed many other works for tape, film, and the theater in the 1950s. Their studio became the home for John Cage's Project of Music for Magnetic Tape, and they assisted in the creation of Cage's first chance piece Williams Mix (1951-52), as well as works by other members of the group such as Earle Brown and Morton Feldman. As a studio for the creation of their own and other composers' works, the Barrons' studio served as a functioning center for electro-acoustic music at a time when there was no institutional support of the medium in the United States. It's curious, then, that, for many years, the Barrons, their studio, and their works were largely overlooked by composers and historians in the field. Fortunately, that injustice has since been corrected, and, in 1997, it was my great honor to present to Bebe and, posthumously, to Louis, the SEAMUS Lifetime Achievement Award. Bebe was involved with SEAMUS from the very beginning of the organization. She was one of the ten original members who responded to my organizational call and met at CalArts in November of 1984 to form the group, and she was SEAMUS's first secretary. There may have been a little strong-arming on my part to get her to be involved so actively, but Bebe was always ready to support the cause of electro-acoustic music in whatever way she could.
Bebe created a firm legacy in her music. If the importance of one's work is to be judged in any regard by it's influence, acceptance, longevity, and innovative qualities, then the score for Forbidden Planet is an enormous success. It remains the most widely known electro-acoustic music work on this planet. For me, Bebe Barron will always be the First Lady of electronic music."

Update: BTW, if you have Netflix, you can watch Forbidden Planet online in IE here.
Bebe Barron on Anais Nin Uploaded on Mar 5, 2008
Sunday, September 13, 2015
An Interview with Barry Schrader
Hi everyone! As you know Barry Schrader will be giving his farewell concert at CalArts on September 26. The following is the beginning of my interview with him. I opted to post the questions and answers as they come in. New QAs will get a new post so you do not miss them and they will be added to this post so we have one central post for the full interview. This should make it easier for all of us to consume in our busy lives, and it will allow you to send in any questions that may come to mind during the interview process. If you have anything you'd like to ask Barry, feel free to send it in to matrixsynth@gmail.com. This is a rare opportunity for us to get insight on a significant bit of synthesizer history, specifically with early Buchla systems, and I'd like to thank Barry for this opportunity. Thank you Barry!
PREVIOUS PAGE
HOME












© Matrixsynth - All posts are presented here for informative, historical and educative purposes as applicable within fair use.
MATRIXSYNTH is supported by affiliate links that use cookies to track clickthroughs and sales. See the privacy policy for details.
MATRIXSYNTH - EVERYTHING SYNTH













© Matrixsynth - All posts are presented here for informative, historical and educative purposes as applicable within fair use.
MATRIXSYNTH is supported by affiliate links that use cookies to track clickthroughs and sales. See the privacy policy for details.
MATRIXSYNTH - EVERYTHING SYNTH